Much has been discussed about Docker, containers, virtualization, microservices and distributed applications. On this post let's recap the essential concepts and review related technologies.
 |
| Photo by chuttersnap on Unsplash |
Virtualization
So let's start with a bit of history. More a less 20 years ago the industry saw a big growth in processing power, memory, storage and a significant decrease in hardware prices. Engineers realized that their applications weren't utilizing the resources effectively so they developed Virtual machines (VMs) and hypervisors to run multiple operating systems in parallel on the same server. |
| Source: Resellers Panel |
A hypervisor is computer software,
firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machines. The computer where the hypervisor runs is called the host, and the VM is called a guest.
The first container technologies
As virtualization grew, engineers realized that VMs were difficult to scale, hard to secure, utilized a lot of redundant resources and maxed out at a dozen per server. Those limitations led to the first containerization tools listed below.- FreeBSD Jails: FreeBSD jails appeared in 2000 allowing the partitioning of a FreeBSD system into multiple subsystems. Jails was developed so that the same server could be sharded with multiple users without securely.
- Google's lmctfy: Google also had their own container implementation called lmcty (Let Me Contain That For You). According to the project page, lmctfy used to be Google’s container stack which now seems to be moved to runc.
- rkt: rkt was another container engine for Linux. rkt has ended and with CoreOS transitioning into Fedora CoreOS. Most of the efforts on that front should be happening into Podman now.
- LXC: released on 2008, the Linux Containers project (LXC) is another container solution for Linux. LXC provides a CLI, tools, libraries and a reference specification that's followed by Docker, LXD, systemd-nspawn and Podman/Buildah.
- Podman/Buildah: Podman and Buildah are also tools to create and manage containers. Podman provides an equivalent Docker CLI and improves on Docker by neither requiring a daemon (service) nor requiring root privileges. Podman's available by default on RH-based distros (RHEL, CentOS and Fedora).
- LXD: LXD is another system container manager. Developed by Canonical, Ubuntu's parent company, it offers pre-made images for multiple Linux distributions and is built around a REST API. Clients, such as the command line tool provided with LXD itself then do everything through that REST API.
Docker
Docker first appeared in 2008 as dotCloud and became open-source in 2013. Docker is by far the most used container implementation. According to Docker Inc., more than 3.5 million Docker applications have been deployed and over 37 billion containerized applications downloaded.Docker grew so fast because it allowed developers to easily pull, run and share containers remotely on Docker Hub as simple as:
docker run -it nginx /bin/bash
Differences between containers and VMs
So what's the difference between containers and VMs? While each VM has to have their own kernel, applications, libraries and services, containers don't as they share some of the host's resources. VMs are also slower to build, provision, deploy and restore. Since containers also provide a way to run isolated services, are lightweight (some are only a few MBs), start fast and are easier to deploy and scale, containers became the standard today.The image below shows a visual comparison between VMs and Containers:
 |
| Source: ZDNnet |
Why Containers?
Here are guidelines that could help you decide if you should be using containers instead of VMs:- containers share the operating system's kernel with other containers
- containers are designed to run one main process, VMs manage multiple sets of processes
- containers maximize the host's resource utilization
- containers faster to run, download and start
- containers are easier to scale
- containers are more portable than VMs
- containers are usually more secure due to the reduced attack surface
- containers are easier to deploy
- containers can be very lightweight (some are just a few MBs)
Containers are not only advantages. They also bring many technical challenges and will require you to
not only rethink how your system is designed but also to use different tools. Look at the
Ecosystem section below to understand.
Usage of Containers
And how much are containers being used? According to the a Cloud Native Computing Foundation survey, 84% of companies today use containers in production, a 15% increase from last year. Another good metric is provided by the Docker Index:Open Collaboration

The Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), part of the Linux Foundation is another significant entity in the area. CNF hosts many of the fastest-growing open source projects, including Kubernetes, Prometheus, and Envoy. CNCF's mission is to promote, monitor and hosts critical components of the global technology infrastructure.
The Technologies
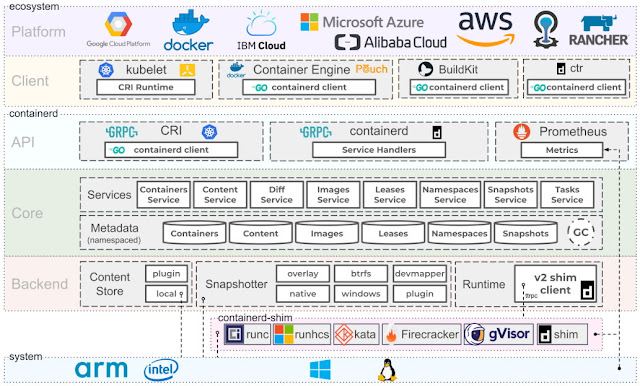
Now let's dive into the technologies used by Docker (and OCI containers in general). The image below shows a detailed overview of the internals of a container. For clarity, we'll break the discussion in user and kernel space.User space technologies
In usersland, Docker and other OCI containers utilize essentially these technologies:- runc: runc is a CLI tool for spawning and running containers. runc is a fork of libcontainer, a library developed by Docker that was donated to the OCI and includes all modifications needed to make it run independently of Docker.
- containerd: containerd is a project developed by Docker and donated to the CNCF that builds on top of runc adding features, such as image transfer, storage, execution, network and more.
- CRI: CRI is the containerd plugin for the Kubernetes Container Runtime Interface. With it, you could run Kubernetes using containerd as the container runtime.
- Prometheus: Prometheus is an open-source systems monitoring and alerting toolkit. Prometheus is an independent project and member of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.
- gRPC: gRPC is an open source remote procedure call system developed by Google. It uses HTTP/2 for transport, Protocol Buffers as the interface description language, and provides features such as authentication, bidirectional streaming and flow control, blocking or nonblocking bindings, and cancellation and timeouts.
- Go: yes, some of the tools are developed in C but Go shines in the area. Most of the open-source projects around containers use Go including: runc, runtime-tools, Docker CE, containerd, Kubernetes, libcontainer, Podman, Buildah, rkt, CoreDNS, LXD, Prometheus, CRI, etc.
Kernel space technologies
In order to provide isolation, security and resource management, Docker relies on the following features from the Linux Kernel:- Union Filesystem (or UnionFS, UFS): UnionFS is a filesystem that allows files and directories of separate file systems to be transparently overlaid, forming a single file system. Docker implements some of them including brtfs and zfs.
- Namespaces: Namespaces are a feature of the Linux kernel that partitions kernel resources so that one set of processes sees one set of resources while another set of processes sees a different set of resources. Specifically for Docker, PID, net, ipc, mnt and ufs are required.
- Cgroups: Cgroups allow you to allocate resources — such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, or combinations of these resources — among groups of processes running on a system.
- chroot: chroot changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name files outside the designated directory tree.
Docker Overview
You probably installed Docker on your machine, pulled images and executed them. Three distinct tools participated on that operation: two local Docker tools and a remote container registry. On your local machine the two tools are:- Docker client: this is the CLI tool you use to run your commands. The CLI is essentially a wrapper to interact with the daemon (service) via a REST API.
- Docker daemon (service): the daemon is a backend service that runs on your machine. The Docker daemon is the tool that performs most of the jobs such as downloading, running and creating resources on your machine.
 |
| Source: Docker Overview |
Remote Registry
And what happens when you push your images to a container registry such as Docker Hub? The next image shows the relationship between client, dameon and the remote registry. |
| Source: Docker Overview |
Images and Containers
Moving lower on the stack, it's time to take a quick look at Docker images. Internally, a Docker image can look like this:- Images are built on layers, utilizing the the union file system.
- Images are readonly. Modifications made by the user are stored on a separate docker volume managed by the Docker daemon. They are removed as soon as you remove the container.
- Images are managed using docker image <operation> <imageid>
- An instance of an image is called a container.
- Containers are managed with the docker container <operation> <containerid>
- You can inspect details about your image with docker image inspect <imageid>
- Images can be created with docker commit, docker build or Dockerfiles
- Every image has to have a base image. scratch is the base empty image.
- Dockerfiles are templates to script images. Developed by Docker, they became the standard for the industry.
- The docker tool allows you to not only create and run images but also to create volumes, networks and much more.
For more information about how to build your images, check the official documentation.
Container Security
Due to the new practices of containers new security measures had to be applied. By default, containers are very reliable on some of the security measures of the host operating system kernel. Docker applies the principle of least privilege to provide isolation and reduce the attack surface. In essence, the best practices around container practice are:- signing containers
- only used images from trusted registries
- harden the host operating system
- enforce the principle of least privilege and do not elevate access to access devices
- offer centralized logging and monitoring
- run automated vulnerability scanning
The Ecosystem
Since this post is primarily about containers I'll defer the discussion of some the ecosystem for the future. However, it's important to list the main areas people working with containers, microservices and distributed applications should learn:- Container Registries: remote registries that allow you to push and share your own images.
- Orchestration: orchestration tools deploy, manage and monitor your microservices.
- DNS and Service Discovery: with containers and microservices, you'll probably need DNS and service discovery so that your services can see and talk to each onther.
- Key-Value Stores: provide a reliable way to store data that needs to be accessed by a distributed system or cluster.
- Routing: routes the communication between microservices.
- Load Balancing: load balancing in a distributed system is a complex problem. Consider specific tooling for your app.
- Logging: microservices and distributed applications will require you to rethink your logging strategy so they're available on a central location.
- Communication Bus: your applications will need to communicate and using a Bus is the preferred way.
- Redundancy: necessary to guarantee that your system can sustain load and keep operating on crashes.
- Health Checking: consistent health checking is necessary to guarantee all services are operating.
- Self-healing: microservices will fail. Self-healing is the process of redeploying services when they crash.
- Deployments, CI, CD: redeploying microservices is different than the traditional deployment. You'll probably have to rethink your deployments, CI and CD.
- Monitoring: monitoring should be centralized for distributed applications.
- Alerting: it's a good practice to have alerting systems on events triggered from your system.
- Serverless: allows you to build and run applications and services without running the servers..
- FaaS - Functions as a service: allows you to develop, run, and manage application functionalities without maintaining the infrastructure.
Conclusion
On this post we reviewed the most important concepts about Docker containers, virtualization and the whole ecosystem. As you probably realized by the lenght of this post, the ecosystem around containers and microservices is huge - and keeps growing! We will cover in more detail much of the topic addressed here on future posts.In the next posts, we will start divining in the details of some of these technologies.
References
- Docker - Get Started
- Docker - Overview
- OCI containers
- What's a Linux container? | Red Hat
- What is Docker and why is it so darn popular?
- Here's how Microsoft is supporting the open-source Docker container model
- Kubernetes jumps in popularity | ZDNet
- Containers march into the mainstream
- Do you really need Kubernetes?
- Helping You and Your Development Team Build and Ship
- Top Six Open Source Tools for Monitoring Kubernetes and Docker
- Open Containers Initiative (OCI) - FAQ
- 2019 CCNF Survey
- What's Envoy?
- containerd, with Derek McGowan
See Also
- Microservices in ASP.NET
- My journey to 1 million articles read
- Adding Application Insights to your ASP.NET Core website
- Configuration in .NET Core console applications
- Building and Hosting Docker images on GitHub with GitHub Actions
- Hosting Docker images on GitHub
- Send emails from ASP.NET Core websites using SendGrid and Azure
- Async Request/Response with MassTransit, RabbitMQ, Docker and .NET core
- How to build and run ASP.NET Core apps on Linux
- 5 tools for Azure Development on Linux